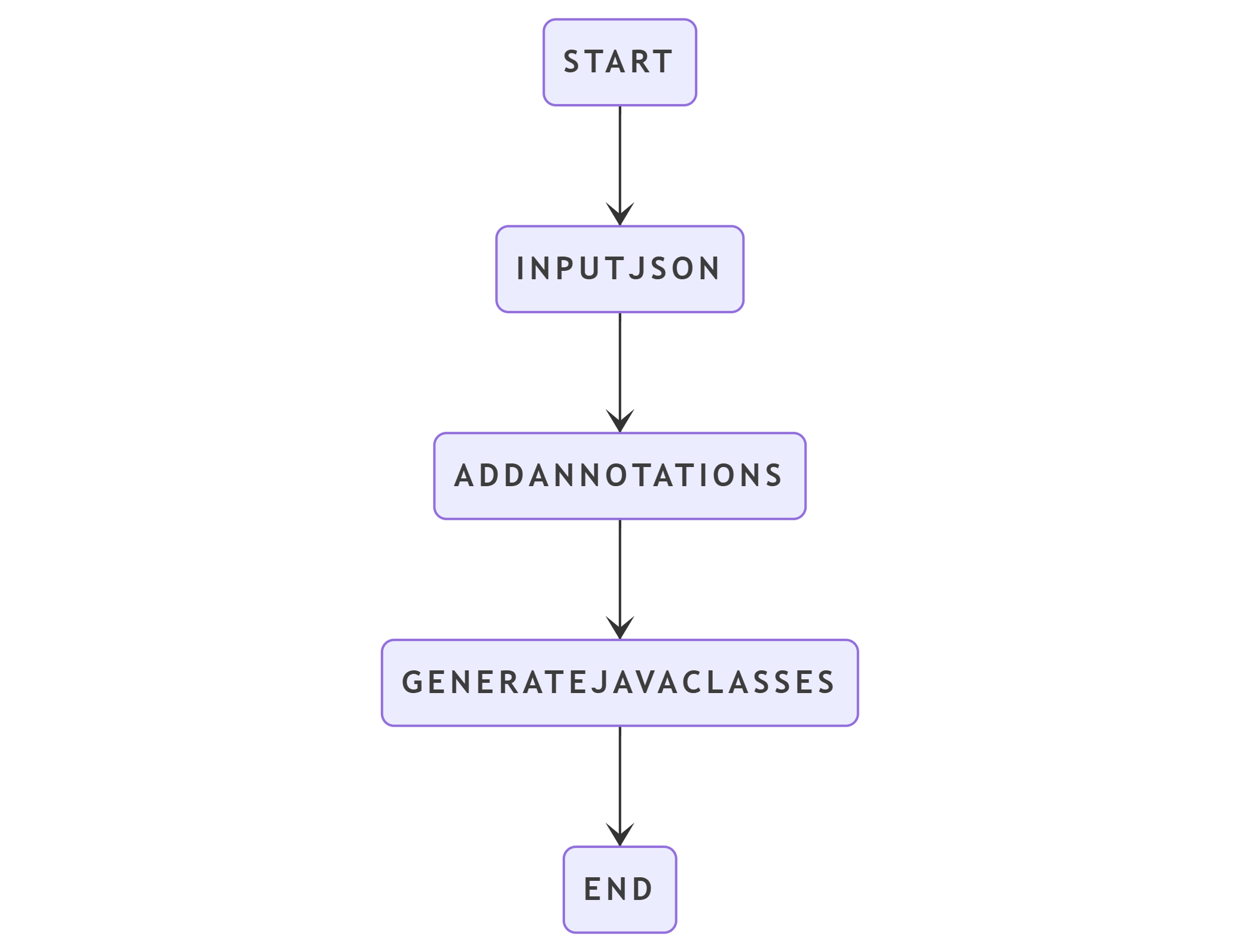
How to generate JSON string to Java Classes ?
The diagram elaborate how to convert JSON to Java classes using our online tool. You have a option whether to include Jackson's @JsonProperty annotations. Simply follow the below steps.
Step 1: Paste the JSON string
Copy your JSON string and paste it into the left side JSON editor.
Ensure the JSON is well-formatted and enclosed in curly braces {}.
Avoid escape characters like backslashes \ that can break structure.
Example JSON:
{
"name": "Alice",
"age": 28,
"isEmployed": true,
"salary": 80000.50,
"occupation": null
}
Step 2: Choose option to Generate Java Classes JSON property
Tick the " JSON Property" checkbox:
- Checked: Adds
@JsonPropertyannotations for each field, ideal when JSON and Java field names differ. - Unchecked: Omits annotations, best when field names already match JSON keys.
Then click the Convert button to generate the matching Java classes.
Step 3: Integrate into your Java project
Copy the generated Java classes into your project or simply click on the Download button to download generated Java class.
Use the Root class as your main model and deserialize with a library like Jackson or Gson.
- Deserialization handles JSON mapping automatically.
- Classes mirror your JSON structure and are ready for immediate use.
Generated Java Class Example (with @JsonProperty):
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
public class Root {
@JsonProperty("name")
public String name;
@JsonProperty("age")
public int age;
@JsonProperty("isEmployed")
public boolean isEmployed;
@JsonProperty("salary")
public double salary;
@JsonProperty("occupation")
public Object occupation;
}
Generated Java Class Example (without @JsonProperty):
public class Root {
public String name;
public int age;
public boolean isEmployed;
public double salary;
public Object occupation;
}
Find the below deserialization example with Jackson:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String myJsonResponse = "{\"name\": \"Alice\", \"age\": 25, \"isEmployed\": true, \"salary\": 60000.50, \"occupation\": null}";
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
try {
Root myDeserializedClass = objectMapper.readValue(myJsonResponse, Root.class);
System.out.println("Name: " + myDeserializedClass.name);
System.out.println("Age: " + myDeserializedClass.age);
System.out.println("Is Employed: " + myDeserializedClass.isEmployed);
System.out.println("Salary: " + myDeserializedClass.salary);
System.out.println("Occupation: " + myDeserializedClass.occupation);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}